What Determines the Maximum Operating Frequency of a Diode?
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.

A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate.
A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used.
Among many uses, diodes are found in rectifiers to convert AC power to DC, demodulation in radio receivers, and can even be used as temperature sensors. A common variant of a diode is a light emitting diode, which is used as electric lighting and status indicators on electronic devices. Diodes may be combined with other components to form logic gates.
Diodes Explained - The basics how diodes work working principle
Topics covered in this article: |
Ⅰ. Simple Basics
1. Junction Capacitance
Diode is mainly junction capacitance, the following picture is a simple diode model.
.jpg)
Figure. 1
2. Reverse Recovery Time
When the voltage abruptly reverses, the diode current in actual applications does not drop to zero right away; instead, a relatively substantial reverse current remains, which must be reduced to 0.1 times the maximum value. The reverse recovery time is time.
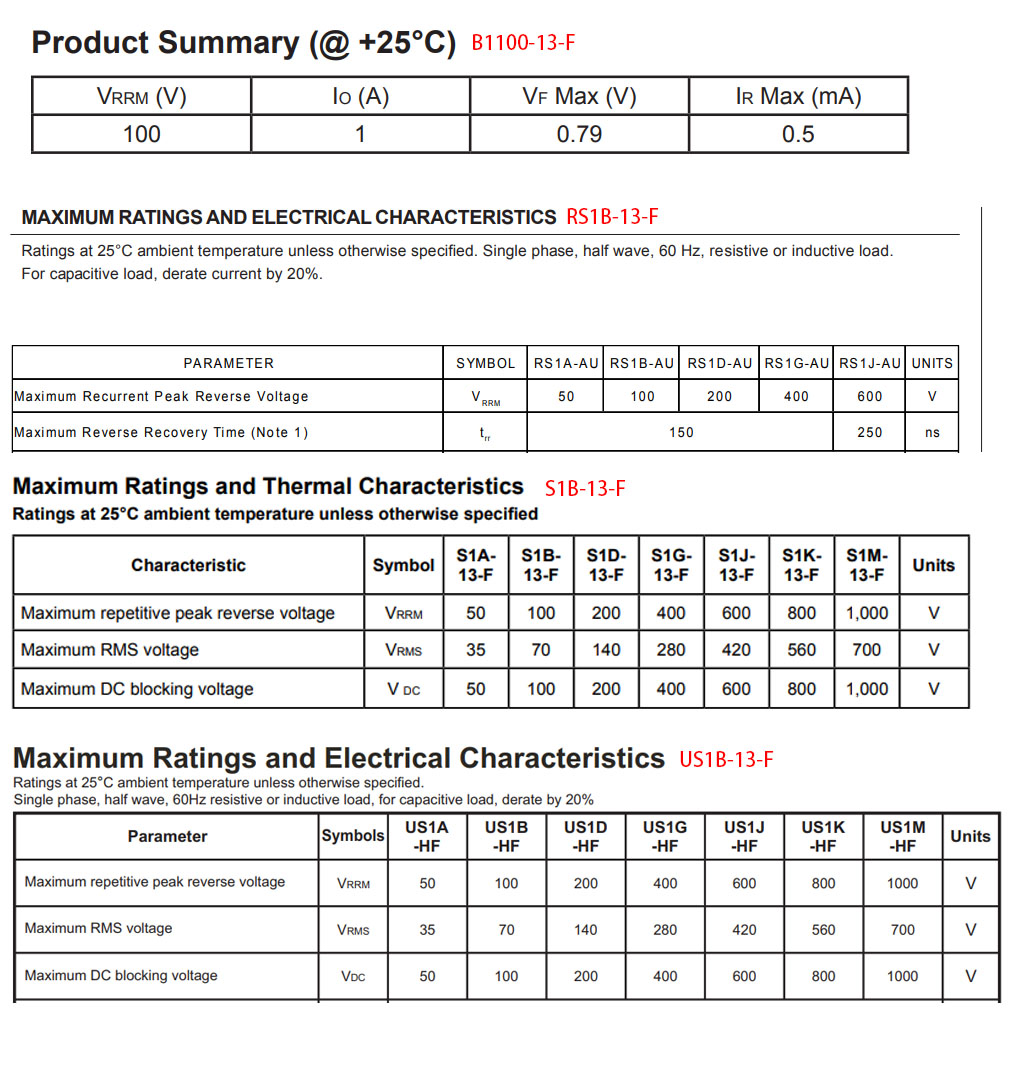
Figure. 2
Ⅱ. Facts
Why can the reverse recovery time never be equal to the charge and discharge time of the junction capacitance?
The junction capacitance and reverse recovery time Trr characteristics for diodes are typically provided by the manufacturer. Now let's compare the characteristics of four distinct diode types: Schottky diodes, and ultra-quick recovery diodes. rapid recovery diodes, and standard diodes,
We ensure that the four manufacturers of the four different types of diodes have the same withstand voltage, packing, and maximum working current in order to make the results more credible. The maximum reverse withstand voltage is 100V, all of the packages are SMA, and the maximum operating current is 1A. The manufacturer chosen here is DIODE Semiconductor.
The models are:
● Schottky diode: B1100-13-F
● Ultra-fast recovery diode: US1B-13-F
● Fast recovery diode: RS1B-13-F
● Ordinary diode: S1B-13-F
Screenshots of these diode parameters are as follows:

Figure. 3
The parameters sorted out are as follows:

Figure. 4
The Schottky diode has the greatest junction capacitance among them, as was previously demonstrated. The Schottky diodes aren't running at the highest frequency, are they? The junction capacitance is the biggest, so why?
Although Schottky diodes' reverse recovery time isn't specified in the standard document, we should all be aware that it is the least.
In a strict sense, the Schottky diode's operation differs from the PN junction diode's in that there is no reverse recovery time. Simply said, because parasitic capacitance exists, there is a maximum operating frequency.
We are aware that various sorts of diodes operate in the following sequence from greatest to lowest operating frequency:
Figure. 5
We now know that
Figure. 6
So it is certain that the length of the reverse recovery time is not determined by the PN junction capacitance.
Ⅲ. Answers to Questions
Returning to the original query, what factor determines the diode's maximum operating frequency?
In fact, it is simple to consider: First off, a high operating frequency cannot be used if the junction capacitance is too large. Because the capacitor's impedance decreases with frequency, the signal passes directly from the capacitor and the diode's reverse cut-off capability is lost.
Second, a high operating frequency is not possible if the reverse recovery time is too long. Because voltage flips more quickly at higher frequencies. The voltage changed again after the reverse bias, the reverse current did not return, and the diode's ability to serve as a reverse cut-off was lost.
Therefore, in general, the maximum operating frequency of the diode will depend on the junction capacitance and reverse recovery time. Exactly who chooses who has more influence.
A Schottky diode's operating frequency is determined by the junction capacitance since the reverse recovery time is so quick.
The reverse recovery time determines the maximum operating frequency of PN junction diodes since it has a far bigger impact than the junction capacitance, which is typically tens of pF.
We also know that Schottky diodes can operate at higher frequencies and have the quickest Schottky speed when compared to PN junction diodes.
In conclusion, The reverse recovery time is not the charging and discharging time of the junction capacitance.






 Need Help?
Need Help?







