A Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is a fundamental electronic component used in a wide range of applications, including amplifiers, switches, and digital logic circuits. MOSFETs are popular due to their high switching speed, low power consumption, and compact size. Here are the basics of MOSFETs:
Structure:
MOSFETs have three terminals: the source, the gate, and the drain.
They are typically made from silicon, with an insulating layer of silicon dioxide (oxide) and a metal gate electrode. Hence, the name Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor.
Operation:
MOSFETs are voltage-controlled devices, meaning their behavior is controlled by the voltage applied to the gate terminal.
There are two types of MOSFETs: N-channel and P-channel, based on the type of charge carriers (electrons or holes) they primarily use for conduction.
N-Channel MOSFET:
In an N-channel MOSFET, electrons are the charge carriers.
When a positive voltage (typically referred to as Vgs) is applied to the gate relative to the source, it creates an electric field that attracts electrons from the source to the channel between the source and drain.
When Vgs exceeds a certain threshold voltage (Vth), the MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow from the source to the drain.
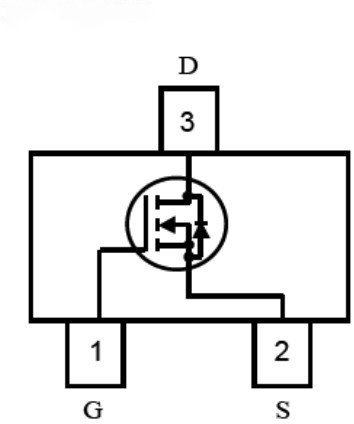
P-Channel MOSFET:
In a P-channel MOSFET, holes are the charge carriers.
It operates in a similar way to the N-channel MOSFET but with reversed voltage polarities. When a negative Vgs is applied, it allows current to flow from the source to the drain.
Modes of Operation:
MOSFETs can operate in three modes: cut-off, triode (or linear), and saturation.
In the cut-off region, the MOSFET is off and doesn't allow current to flow.
In the triode region, it operates as an amplifier, allowing a controlled amount of current to flow between the source and drain.
In the saturation region, it's fully turned on, and current flows freely between the source and drain.
Applications:
N-channel and P-channel MOSFETs are used in various applications, including digital logic circuits, voltage amplification, switching applications (such as power switches in electronic devices), and more.
MOSFETs are commonly used in integrated circuits (ICs) and discrete components due to their versatility and efficiency.
Advantages:
MOSFETs offer high input impedance, making them easy to drive with low-power signals.
They consume very little power when in the off state, reducing energy wastage.
They can switch at high speeds, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Disadvantages:
MOSFETs are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD) and voltage spikes, requiring protective measures.
They have a limited voltage handling capability compared to some other power electronic devices like IGBTs.
Understanding the basics of MOSFET operation is essential for designing and using electronic circuits effectively. The specific characteristics and parameters of a MOSFET can vary among different models and manufacturers, so always refer to datasheets for detailed information when working with them in practical applications.




 Need Help?
Need Help?







