Catalog
| Ⅰ CPU |
| Ⅱ GPU |
| Ⅲ DPU |
| Ⅳ VPU |
| Ⅴ APU |
| Ⅵ BPU |
| Ⅶ EPU |
| Ⅷ FPU |
| Ⅸ HPU |
| Ⅹ IPU |
| Ⅺ PPU |
| Ⅻ QPU |
| XⅢ SPU |
The Central Processing Unit (CPU), also known as the processor, is one of the core components of a computer system.
Central Processing Unit (CPU) consists of the following features
◆CPU is considered as the brain of the computer.
◆CPU performs all types of data processing operations.
◆Stores data, intermediate results, and instructions (program).
◆Control the operation of all parts of the computer.
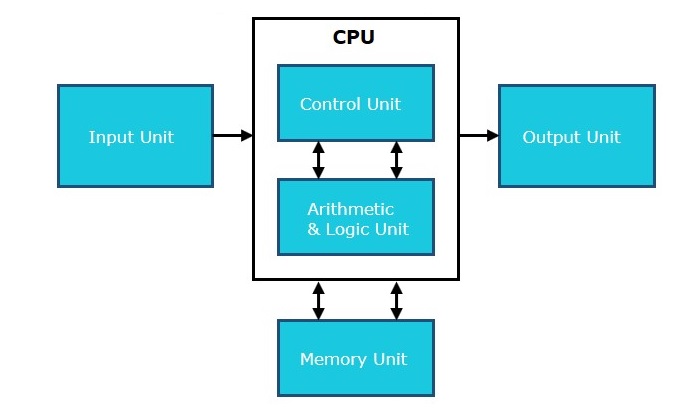
CPU itself has following three components.
◆Memory or Storage Unit - store instructions, data, and intermediate results.
◆Control Unit - controls the operations of all parts of the computer but does not carry out any actual data processing operations.
◆ALU - Consist of arithmetic and logic section, perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, comparing, selecting, matching, and merging of data.
These two companies, Intel Corporation and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), have historically dominated the consumer CPU market.
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) was originally developed to meet the needs of graphics rendering. In the GPU chip market, Nvidia controls approximately 80% of the global market. Its GPU chips are mainly used in the gaming market, but now its role is much more than that. Due to its parallel processing capabilities, the GPU, which has been advancing rapidly, is like a fearless teenager, showing unlimited possibilities. GPU has been widely used in many fields such as deep learning and scientific computing. This computing power can not only accelerate graphics processing, but also share the burden of the CPU on other tasks, such as data analysis, machine learning, etc.
The graphics processing unit, or GPU, was originally developed to meet the urgent need for graphics rendering, but now it has become much more than that, becoming one of the core forces driving modern computing. Thanks to its excellent parallel processing capabilities, GPU, like a fearless teenager, has been making rapid progress in gaming, mining, AI and other fields, showing unlimited possibilities. Today, GPUs have widely penetrated into key fields such as deep learning and scientific computing, becoming an indispensable part of these fields.
Especially in today's era of artificial intelligence, the extensive and in-depth application of generative AI marks the arrival of a technological revolution. In this context, the importance of the graphics processing unit (GPU) has gradually surpassed the central processing unit (CPU) and has taken the center stage of history.
As the world's largest GPU supplier, NVIDIA occupies approximately 80% of the global GPU market share. On June 13, 2023, Nvidia's market value exceeded the trillion-dollar mark for the first time, making it the fifth-largest market value company in the United States, second only to Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet and Amazon. This milestone highlights the health and growth momentum of the GPU industry, while also signaling the important role it will continue to play in the future.
In the past few years, Nvidia's focus has shifted to the data center market. The revenue data for the second quarter of 2023 shows a very striking phenomenon. Until 2023, the market share of CPUs in data centers has been significantly higher than that of GPUs. In fact, even in the first quarter of 2023, Nvidia's data center business revenue ($4.2 billion) still failed to exceed the combined revenue of Intel and AMD. But in the second quarter, the situation has changed dramatically. In the data center business, the two major CPU giants Intel and AMD have revenue of US$4 billion and US$3 billion respectively. In stark contrast, NVIDIA's data center business revenue exceeds $10 billion, a figure that even exceeds the combined revenue of Intel and AMD. This data fully shows that the status of GPU is rising rapidly and has surpassed CPU in some areas.
DPU is specially designed to handle large amounts of data and information. It can effectively process and analyze data and improve the performance of data centers and cloud computing platforms. According to Nvidia, the DPU should be able to complete the following three major tasks:
Offload: Taking over infrastructure tasks from the server CPU so that more CPU power is available for running applications.
Acceleration: Use hardware acceleration in the DPU chip to run infrastructure functions faster than the CPU.
Isolation: Moving critical data plane and control plane functions to separate domains on the DPU both relieves the server CPU of work and protects functions if the CPU or its software is compromised.
Much of the DPU development to date has been for hyperscale. Going forward, the use of DPUs in data centers and elsewhere in enterprise networks is expected to grow. One possible way to do this is by merging DPU technology with network switches—a combination of technologies that AMD Pensando calls “intelligent switches.” "We believe smart switches are the easiest way for enterprises to absorb DPU technology, as it allows them to retire older equipment and bring significant technology and scale to their networks," said Soni, chief commercial officer, Network Technology and Solutions Group, AMD Pensando Jiangdani said.
The DPU market is growing steadily due to the growing demand for artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, IoT, 5G and complex cloud architectures. As demand for data-intensive applications continues to increase, computing architectures will continue to evolve, requiring faster, more efficient, and more secure data processing. Many chip players have emerged in the DPU market. The main suppliers include foreign Nvidia, Marvell, Fungible (acquired by Microsoft), Broadcom, Intel, Resnics and AMD Pensando. Domestic ones include Zhongke Yushu, Xinqiyuan Yunbao Intelligent , Yunmaixinlian and so on.
According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global data processing unit market is expected to reach $5.5 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 26.9% from 2022 to 2031. As a result, DPUs may move from being an optional component today to a necessary industry standard for next-generation computing.
With the popularization of video content and the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, the video processing unit (VPU) has become a new star in the current technology field.
VPU (Video Processing Unit) is specially designed to handle video tasks. It can efficiently handle tasks such as video encoding and decoding, image processing and machine vision. By offloading these tasks from the CPU or GPU, the VPU improves the overall efficiency and performance of the system, while also offloading the CPU or GPU so they can focus on other tasks. Moreover, such VPUs usually have many advantages such as high performance, low power consumption and low latency. According to SemiAnalysis' analysis of VPU chip manufacturer NETINT, compared with CPUs and GPUs, the density and power of VPUs are The power consumption is unmatched by CPU and GPU. The emergence of VPU can be said to have brought unprecedented accelerated computing capabilities to video industry applications.

The current widespread application of high-definition video technologies such as 4K and 8K has caused the computational burden of video processing to continue to rise, making high-performance VPUs an essential tool for industry development. Currently, Internet giants including Google, Meta, ByteDance and Tencent have taken aim at this chip. At the same time, AMD released a new dedicated media accelerator and video encoding card for data centers in April this year - Alveo MA35D, while Intel integrated the VPU into its 14th generation Core Meteor lake processor. In addition to cloud and data centers, terminals have also become the main carrier of videos and games, and mobile phone manufacturers are increasingly pursuing video or image quality. In this regard, vivo/Xiaomi use video chips as the entry point for self-research, and third-party video chip suppliers such as Pixelworks/Zidian Semiconductor are also beginning to usher in development opportunities.
In the future, the video processing chip market is expected to continue to grow, especially in the fields of edge computing, Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G communications. Efficient and low-power video processing chips will become key components in these application areas.
1. Accelerated Processing Units
The Chinese name is acceleration processor, which is a future-focused product launched by AMD in 2011. For the first time, the processor and independent graphics core are built on one chip to collaborate in calculations and accelerate each other, so that tasks can be flexibly distributed between the CPU and GPU to improve efficiency.
2. Audio Processing Unit
APU can also refer to Audio Processing Unit, a unit dedicated to processing sound data. The Audio Processing Unit is a processor on the sound card that can be used to process sound data. Since surround sound processing is becoming more and more important in modern computers (especially home systems and game enthusiasts), a specialized sound processor is needed. core processor.
1. Branch Processing Unit
BPU (Branch Processing Unit) is the area in the CPU used for branch processing.
2. Brain Processing Unit
Brain Processor. The BPU is a custom chip developed by Horizon, an AI chip used for autonomous driving.
1. EPU (Emotion Processing Unit)
This is also the first time I heard the word EPU. EPU was proposed by Emoshape Company. Emoshape is a company dedicated to providing technology that can teach intelligent machines to interact with humans. EPU is based on microcontroller (MCU) design and promotes nearly unlimited cognitive processes to generate real emotional responses in artificial intelligence (AI), robotics and consumer electronics devices. EPU is an extension of Ekman's theory, which uses the evolutionary theory of emotion to identify 12 major emotions.
2. EPU (Energy Processing Unit)
EPU is a real-time system energy-saving chip that automatically detects the current system load and intelligently adjusts power usage, providing power optimization for the entire system, reducing fan noise, and extending the service life of software components. Concept proposed by ASUS.
Ⅷ FPU (Floating Processing Unit)
Module for doing floating point operations
Ⅸ HPU (Holographic Processing Unit)
Holographic Processor. Microsoft HoloLens is the world's first independent holographic computer device, capable of providing high-definition holographic images. The secret lies in the Holographic Processing Unit (HPU) carried by HoloLens, which is a custom chip that can process and Interact data streaming from different sensors and Intel Atom.
Ⅹ IPU (Intelligence Processing Unit)
The concept first proposed by Graphcore, a British AI chip startup, is an intelligent processor. Founded in 2016 and headquartered in Bristol, UK, Graphcore's main business is designing processors for AI applications and providing product support for applications such as cloud services.
Ⅺ PPU (Physics Processing Unit)
Physical computing processor. PPU is a processor that simulates physical calculations. The CPU is to achieve faster computing speed, and the GPU is to achieve better image effects. Then the PPU is used to communicate between the virtual electronic world and the ubiquitous physical reality to make the picture more realistic. , close to reality. The concept of PPU was first proposed at GDC2005.
Ⅻ QPU (Quantum Processing Unit)
Quantum processors use quantum superposition to quickly traverse various possibilities of a problem and find the correct answer. QPU computing power increases with the power exponential 2n as the number of bits n increases. At present, both domestic and foreign countries are in the exploratory stage in the field of quantum computing.
NeuroBlade, an Israeli start-up chip company founded in 2018, has developed a dedicated processor architecture, which they call SPU (SQL Processing Unit). The company aims to become the "Nvidia of data analytics." The SPU is mainly used to accelerate SQL instruction processing. The company's CEO said that by using a specially designed processor to accelerate SQL processing, end-to-end SQL analysis acceleration can be achieved. In terms of deployment, the chip plugs in via the PCIe bus of the host server and is able to transparently take over SQL-related processing without modifying the host application software.
SPU supports common columnar file formats. When a query request is sent from the query engine (that is, a query request is issued from the database management system), the SPU can directly access and process the data files stored on the local storage device. After processing the data file, the SPU will send the processing results back to the query engine in the form of a native query engine layout.
NeuroBlade is in talks with multiple large hyperscale providers and has won a contract with one company for thousands of SPU cards. For example, NeuroBlade also cooperates with Dell to distribute SPU card products in PowerEdge servers. According to them, hyperscale enterprises using this SQL processing unit (SPU) to offload x86 CPUs running analytical workloads can achieve 100x or more job acceleration and save millions of dollars annually. Among NeuroBlade customers, there are also storage customers. Kioxia has successfully configured its NeuroBlade Hardware Enhanced Query System (HEQS) in its CM7 series enterprise NVMe SSDs, which they say can enable customers to take full advantage of high-performance SSDs. throughput potential, thereby improving query performance up to 100x.




 Need Help?
Need Help?







